环境投入产出分析
-
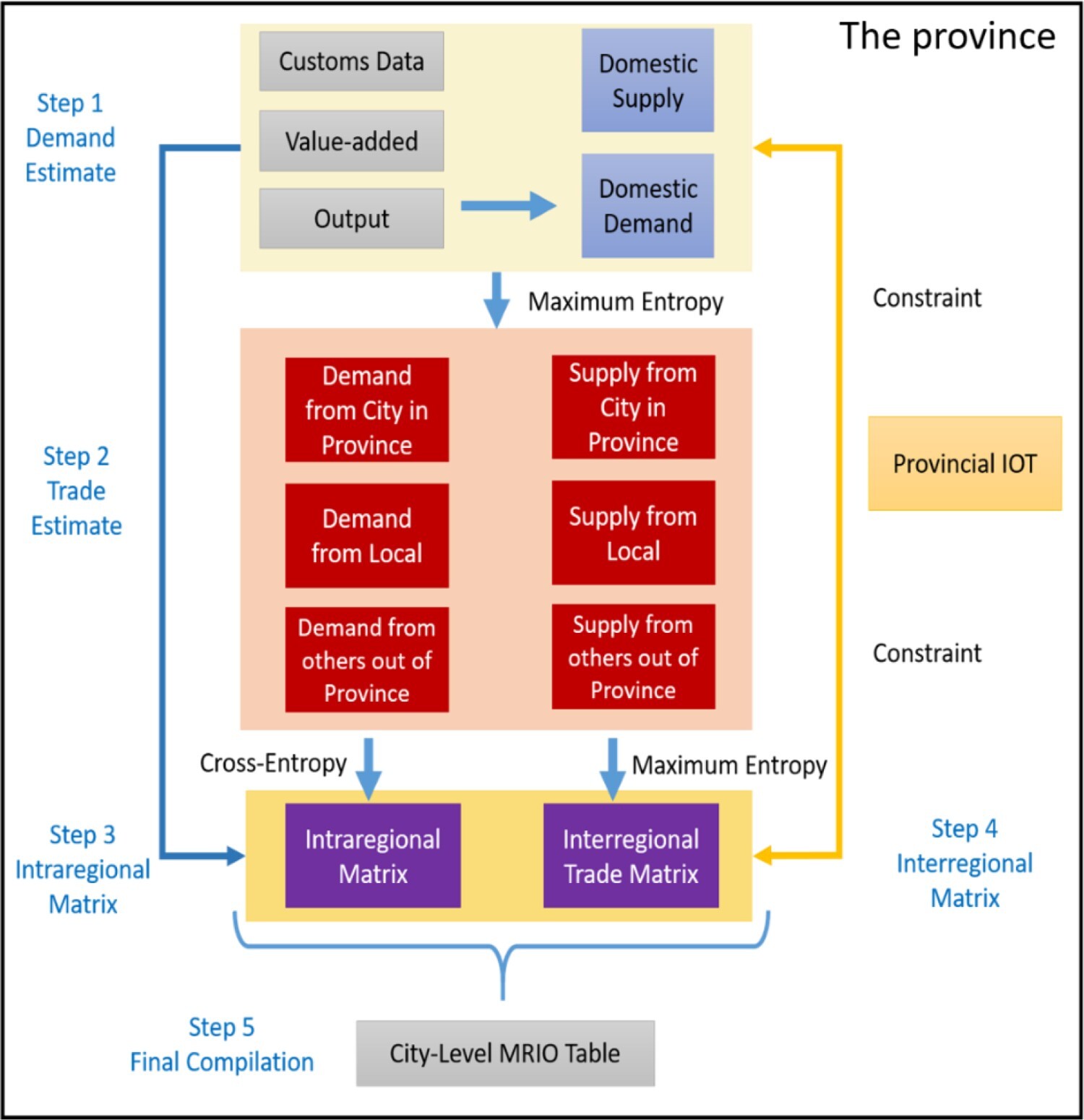
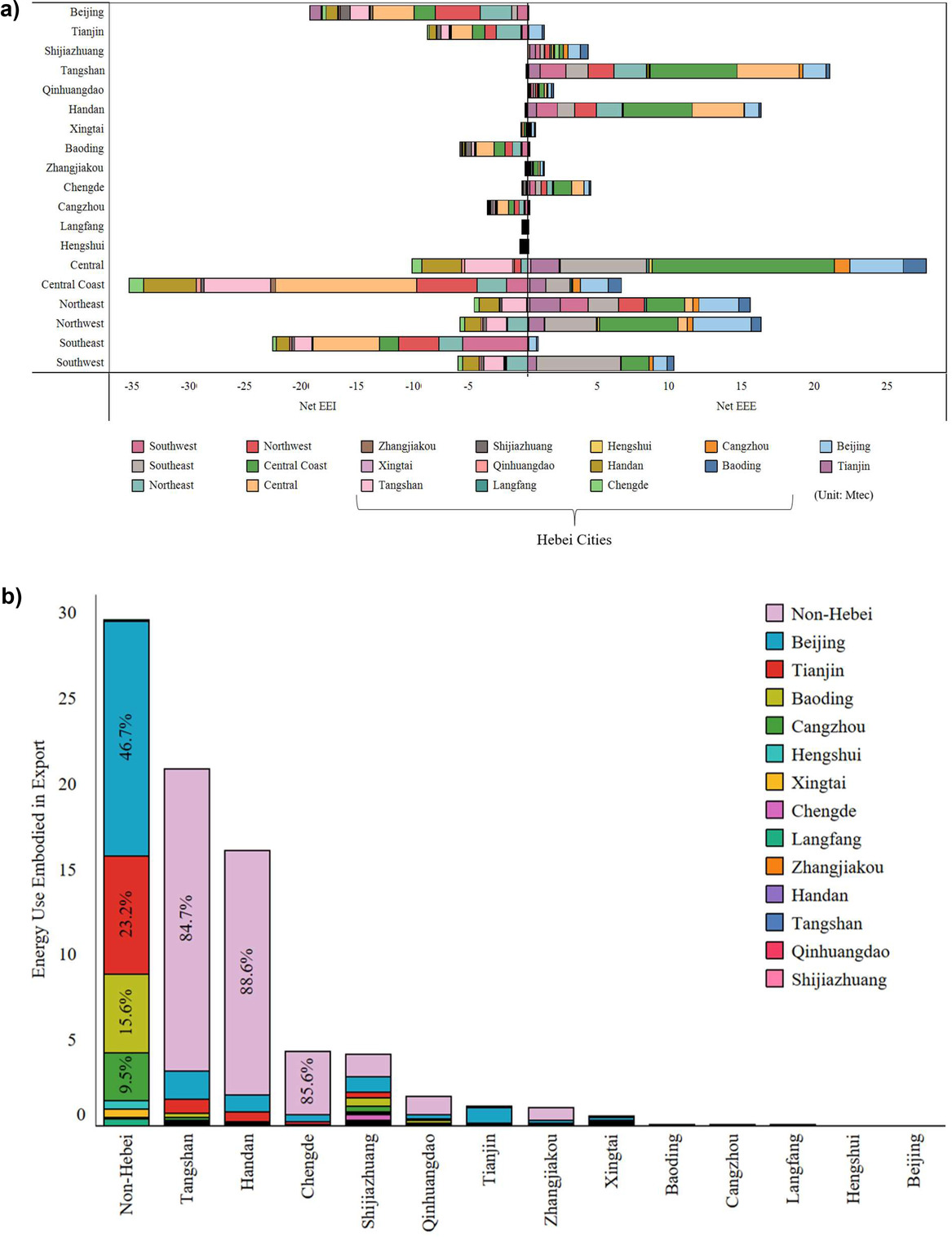
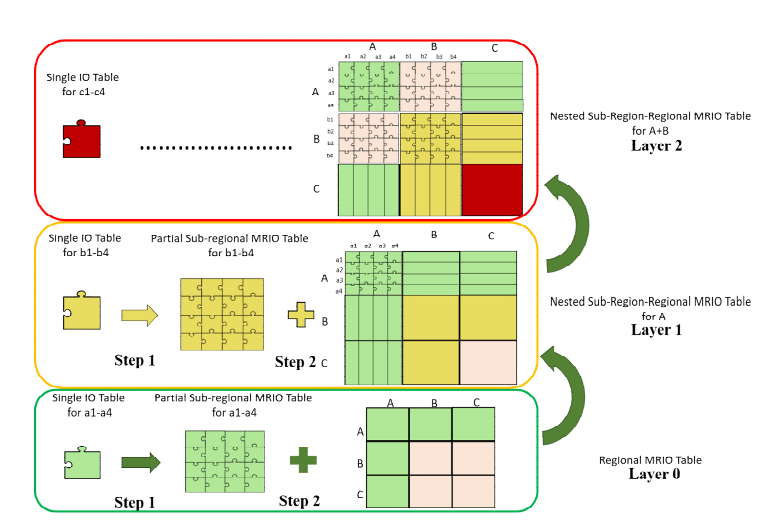
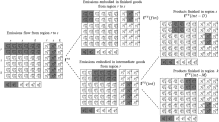
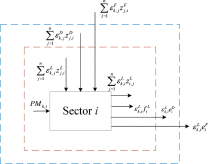
Entropy-based Chinese city-level MRIO table framework
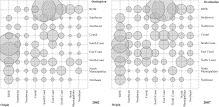
Cities are pivotal hubs of socioeconomic activities, and consumption in cities contributes to global environmental pressures. Compiling city-level multi-regional input-output (MRIO) tables is challenging due to the scarcity of city-level data. Here we propose an entropy-based framework to construct city-level MRIO tables. We demonstrate the new construction method and present an analysis of the carbon footprint of cities in China's Hebei...
-
Full-scale, near real-time multi-regional input–output table for the global emerging economies (EM
Multi-regional input–output (MRIO) models are widely used to analyze the economic interdependencies between regions in the context of global trade and environmental research. MRIO tables enable us to teleconnect the sectors in different regions along the supply chain and track both direct and indirect impacts of global production. Yet emerging economies—despite reshaping international trade patterns and playing an increasingly import...
-
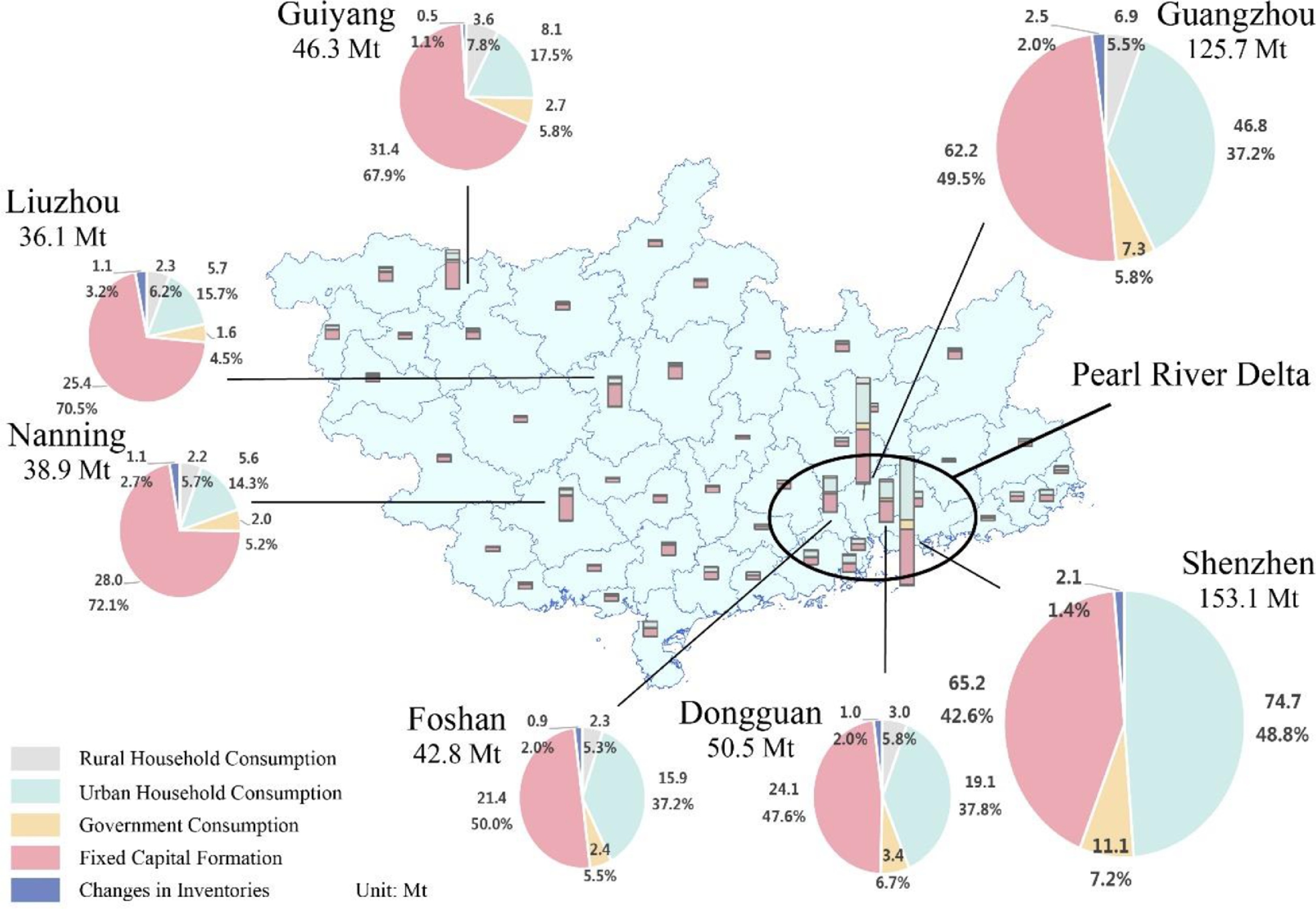
Cities are leading carbon mitigation but are heterogeneous in their mitigation policies due to diffe
Cities are leading carbon mitigation but are heterogeneous in their mitigation policies due to different socioeconomic backgrounds. Given that cities are increasingly inextricably linked, formulating mitigation policies of different cities cannot be easily achieved without comprehensive carbon inventories, who taking the inter-city supply chains into account. The Pearl River Basin is one of the important economic zones in China, with hug...
-
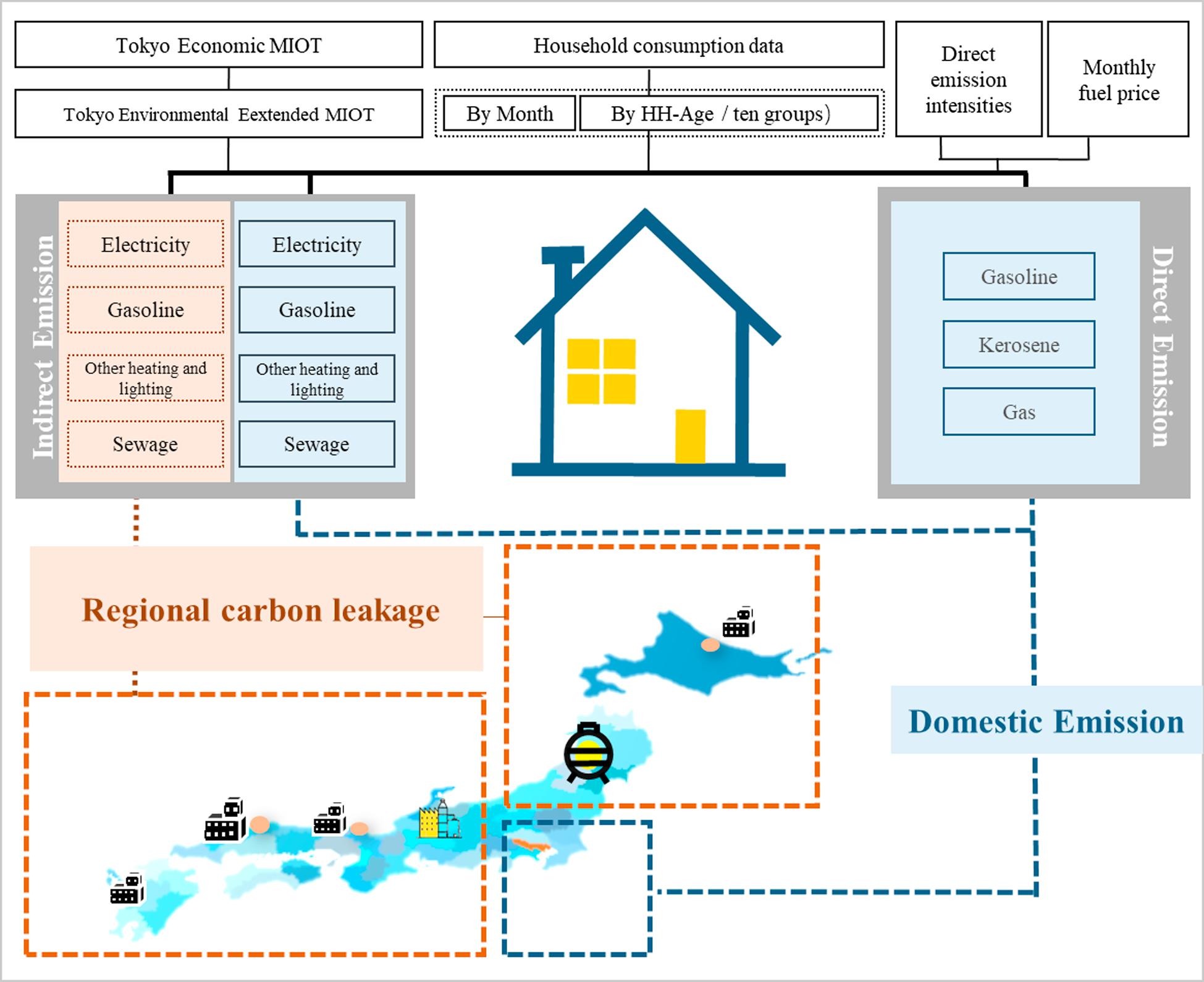
Unequal age-based household emission and its monthly variation embodied in energy consumption–A ca
City is the main place to consume goods and services throughout the world. Among the various consumption terminals, household-level consumption is highly behavior driven, which can be affected by various factors such as household income level, age, living environment etc. However, city-level household emissions characteristics are still not fully understood due to the complexity of consumption behaviors and the lack of the supply chain’...
-
Linking city-level input–output table to urban energy footprint: Construction framework and applic
Multiregion input–output (MRIO) models have become increasingly important in economic and environmental analysis. However, the current resolution of most MRIO models fails to capture the heterogeneity between subregions, especially in cities. The lack of city-level MRIO tables has impeded the accomplishment of city-level studies and hampered the understanding of the relationship between urban growth and consumption, and teleconnection...
-
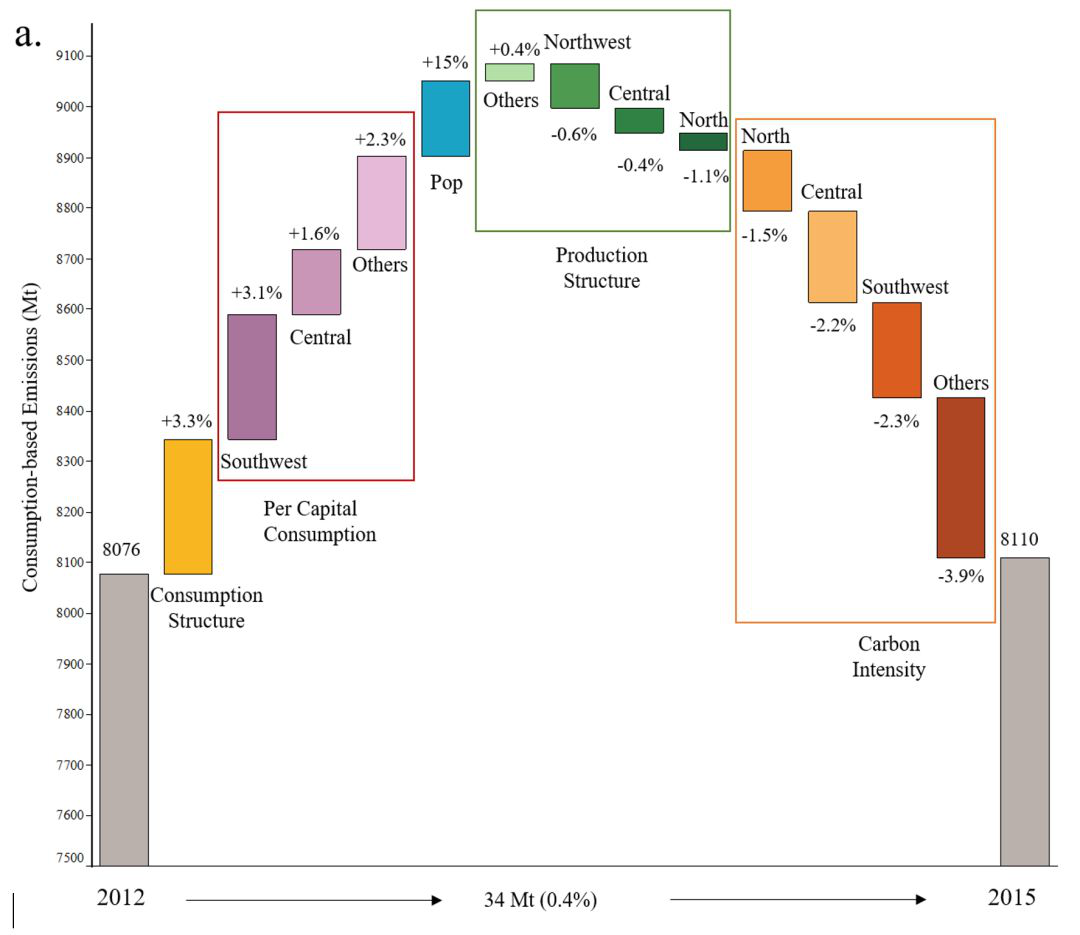
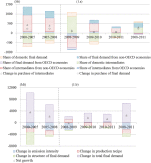
Regional determinants of China's consumption-based emissions in the economic transition
China has entered the economic transition in the post-financial crisis era, with unprecedented new features that significantly lead to a decline in its carbon emissions. However, regional disparity implies different trajectories in regional decarbonisation. Here, we construct multi-regional input-output tables (MRIO) for 2012 and 2015 and quantitatively evaluate the regional disparity in decarbonisation and the driving forces during 201...
-
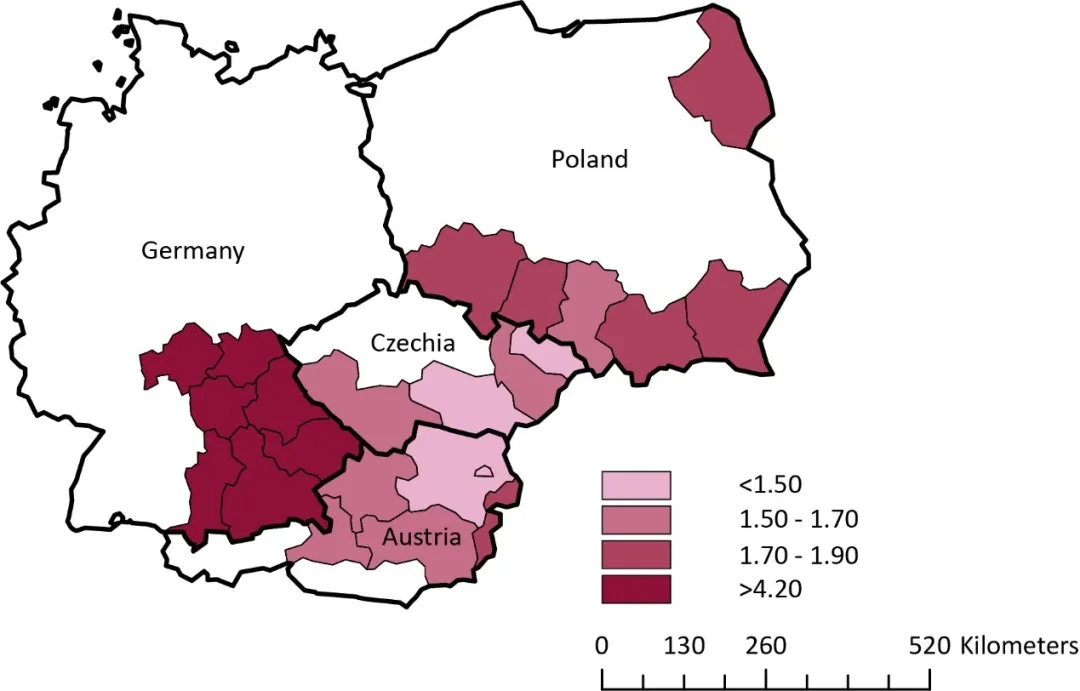
Flood Footprint Assessment: A Multiregional Case of 2009 Central European Floods
Hydrometeorological phenomena have increased in intensity and frequency in last decades, with Europe as one of the most affected areas. This accounts for considerable economic losses in the region. Regional adaptation strategies for costs minimization require a comprehensive assessment of the disasters ’ economic impacts at a multiple ‐ region scale. This article adapts the flood footprint method for multiple-region assessment of to...
-
Methodology and application of flood footprint accounting in a hypothetical multiple two-flood event
Multiple natural disasters are becoming ever more frequent around the world, with both climate change and rapid urbanization increasing the risk of such disasters in human society. Comprehensive analysis of the economic impact of multiple disasters on the industrial and economic system has become an urgent and essential part of urban recovery and sustainable development. However, there is a lack of studies that focus on assessing the in...
-
Flood footprint assessment: a new approach for flood-induced indirect economic impact measurement an
Flooding in one location can impact the entire production chain of a regional economy. Neglecting the knock-on costs of this risks ignoring the economic benefits and beneficiaries of flood risk management interventions. However, economic consequence assessments in the existing studies are restricted to direct economic impact as there is not a generally accepted quantitative method to assess indirect economic impacts. This paper presents...
-
Linking city-level input-output table to urban energy footprint:Construction framework and applicati
Multiregion input-output (MRIO) models have become increasingly important in economic and environmental analysis. However, the current resolution of most MRIO models fails to capture the heterogeneity between subregions, especially in cities. The lack of city-level MRIO tables has impeded the accomplishment of city-level studies and hampered the understanding of the relationship between urban growth and consumption, and teleconnections ...
-
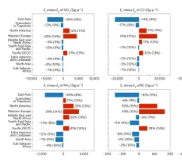
Temporal change in India’s imbalance of carbon emissions embodied in international trade
In India, rapid industrialization and reorganization of the global supply chain are driving economic growth, accompanied by increasing exports and carbon emissions. India is poised to succeed China as the next world manufactory, which will lead to huge emissions in the country. To formulate appropriate emission mitigation measures, it is necessary to further understand the temporal change in India’s emissions at the sectoral level fro...
-
Energy and carbon intensity: A study on the cross-country industrial shift from China to India and S
The potential relocation of various industrial sectors from China to India and countries of the SE Asian region presents low cost opportunities for manufacturers, but also risks rising for energy demand and CO 2 emissions. A cross-country shift of industrial output would present challenges for controlling emissions since India and SE Asian countries present higher industrial emissions intensity than China. We find that although there is...
-
The role of intermediate trade in the change of carbon flows within China
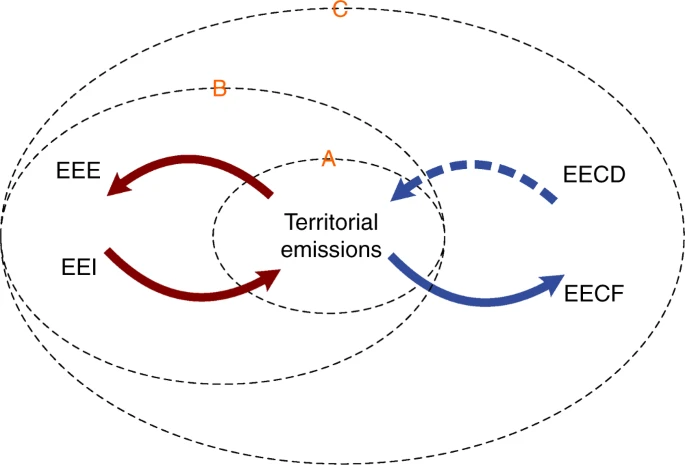
In recent years, evaluating the emissions embodied in trade (EEIT) has become an important area of policy and research. Multiregional input-output (MRIO) analysis, which links producers and final consumers, is a widely-used method for quantifying the EEIT. However, the role of intermediate trade in driving changes in the EEIT is still not fully incorporated in MRIO analysis and as a result poorly understood. Here, we present a framework ...
-
Carbon emissions of cities from a consumption-based perspective
Carbon emission inventories are the foundations of climate change mitigation and adaptation in cities. In this study, we estimated production-based CO 2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion and industrial processes in eleven cities in Hebei Province of China in 2012 and used input-output theory to measure their consumption-based CO 2 emissions. By comprehensively comparing production- and consumption-based emissions, we found that six d...
-
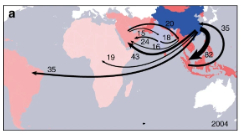
The rise of South–South trade and its effect on global CO2 emissions
Economic globalization and concomitant growth in international trade since the late 1990s have profoundly reorganized global production activities and related CO 2 emissions. Here we show trade among developing nations (i.e., South–South trade) has more than doubled between 2004 and 2011, which reflects a new phase of globalization. Some production activities are relocating from China and India to other developing countries, particular...
-
Origin and Radiative Forcing of Black Carbon Aerosol: Production and Consumption Perspectives
Air pollution, a threat to air quality and human health, has attracted ever-increasing attention in recent years. In addition to having local influence, air pollutants can also travel the globe via atmospheric circulation and international trade. Black carbon (BC), emitted from incomplete combustion, is a unique but representative particulate pollutant. This study tracked down the BC aerosol and its direct radiative forcing to the emissi...
-
The global CO2 emission cost of geographic shifts in international sourcing
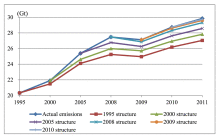
In this paper we simulated the global direct CO 2 emission cost of geographic shift of international sourcing for the period 1995–2011 by comparing the scenarios with and without geographic shift. Our simulations indicate that in 2011, had the share of trade by the sourcing economy remained at the level of 1995, 2000, 2005, and 2008 whereas the global final demand remained the same, global CO 2 emissions in production processes would h...
-
Consumption-based greenhouse gas emissions accounting with capital stock change highlights dynamics
Traditional consumption-based greenhouse gas emissions accounting attributed the gap between consumption-based and production-based emissions to international trade. Yet few attempts have analyzed the temporal deviation between current emissions and future con-sumption, which can be explained through changes in capital stock. Here we develop a dynamic model to incorporate capital stock change in consumption-based accounting. The new mode...
-
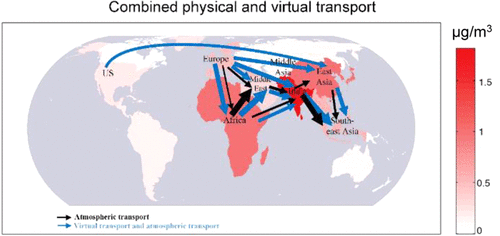
Transboundary health impacts of transported global air pollution and international trade
Millions of people die every year from diseases caused by exposure to outdoor air pollution. Some studies have estimated premature mortality related to local sources of air pollution, but local air quality can also be affected by atmospheric transport of pollution from distant sources. International trade is contributing to the globalization of emission and pollution as a result of the production of goods (and their associated emissions)...
-
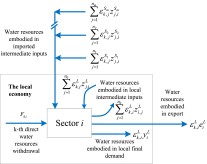
Multi-scale input-output analysis of consumption-based water resources: Method and application
This work develops a method of multi-scale input-output analysis for the embodied water accounting of an economy. This method can distinguish between the different virtual water contents of imported and local products and is therefore capable of estimating the virtual water that is embodied in trade. As a simplified model rather than a multi-regional input-output analysis, this method substantially minimizes the data requirements. With t...
-
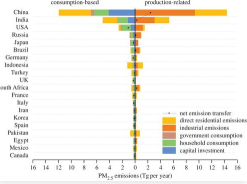
Chinese CO2 emission flows have reversed since the global financial crisis
This study seeks to estimate the carbon implications of recent changes in China's economic development patterns and role in global trade in the post-financial-crisis era. We utilised the latest socioeconomic datasets to compile China's 2012 multiregional input-output (MRIO) table. Environmentally extended input-output analysis and structural decomposition analysis (SDA) were applied to investigate the driving forces behind changes in CO ...
-
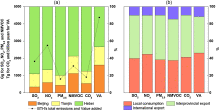
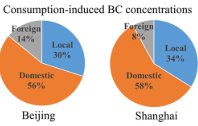
The consumption-based black carbon emissions of China's megacities
A growing body of literature discusses the CO 2 emissions of cities. Still, little is known about black carbon (BC), a short-lived warming agent. Identifying the drivers of urban BC emissions is crucial for targeting cleanup efforts. A consumption-based approach enables all emissions to be allocated along the production chain to the product and place of final consumption, whereas a production approach attributes emissions to the place w...
-
The global CO2 emissions growth after international crisis and the role of international trade
In this paper, we decompose the driving forces of global CO 2 emissions for the post-crisis era 2008–2011 from both production-based and consumption-based aspects. The results suggest that non-OECD economies have become the major drivers for the rapid global growth of CO 2 emissions after the crisis. More specifically, the increasing consumption and investment of non-OECD economies, as well as stagnation of their emission intensity red...
-
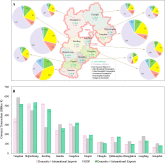
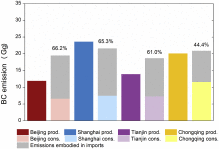
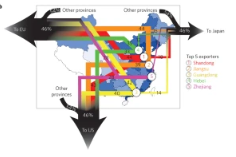
Environment-economy tradeoff for Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei’s exports
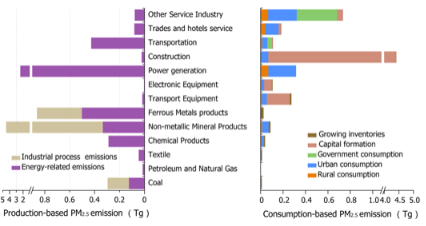
The trade of goods among regions or nations associated with large environmental consequences. Yet balancing economic gains and environmental consequences induced by trade is still hindered by a lack of quantification of these two factors, especially for the environmental problems those are more locally oriented, such as the atmospheric pollution. Based on an environmental input–output analysis for 2010, we contrast economic gains (valu...
-
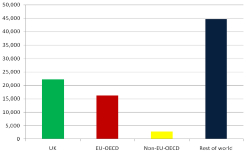
Virtual Water Flows in the EU27: A Consumption‐based Approach
The use of water resources has traditionally been studied by accounting for the volume of water removed from sources for specific uses. This approach focuses on surface and groundwater only and it ignores that international trade of products with substantial amounts of embodied water can have an impact on domestic water resources. Using current economic and environmental data, we conduct a consumption‐based assessment of virtual water ...
-
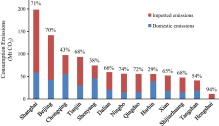
Consumption-based emission accounting for Chinese cities
Most of China’s CO 2 emissions are related to energy consumption in its cities. Thus, cities are critical for implementing China’s carbon emissions mitigation policies. In this study, we employ an input-output model to calculate consumption-based CO 2 emissions for thirteen Chinese cities and find substantial differences between production- and consumption-based accounting in terms of both overall and per capita carbon emissions. Ur...
-
Globalization and pollution: tele-connecting local primary PM2.5 emissions to global consumption
Globalization pushes production and consumption to geographically diverse locations and generates a variety of sizeable opportunities and challenges. The distribution and associated effects of short-lived primary fine particulate matter (PM 2.5 ), a representative of local pollution, are significantly affected by the consumption through global supply chain. Tele-connection is used here to represent the link between production and consump...
-
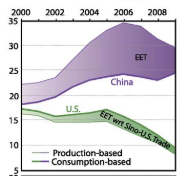
Targeted opportunities to address the climate–trade dilemma in China
International trade has become the fastest growing driver of global carbon emissions, with large quantities of emissions embodied in exports from emerging economies. International trade with emerging economies poses a dilemma for climate and trade policy: to the extent emerging markets have comparative advantages in manufacturing, such trade is economically efficient and desirable. However, if carbon-intensive manufacturing in emerging ...
-
Global climate forcing of aerosols embodied in international trade
International trade separates regions consuming goods and services from regions where goods and related aerosol pollution are produced. Yet the role of trade in aerosol climate forcing attributed to different regions has never been quantified. Here, we contrast the direct radiative forcing of aerosols related to regions’ consumption of goods and services against the forcing due to emissions produced in each region. Aerosols assessed in...
-
Interprovincial Reliance for Improving Air Quality in China: A Case Study on Black Carbon Aerosol
Black carbon (BC) is of global concern because of its adverse effects on climate and human health. It can travel long distances via atmospheric movement and can be geographically relocated through trade. Here, we explored the integrated patterns of BC transport within 30 provinces in China from the perspective of meteorology and interprovincial trade using the Weather Research and Forecasting with Chemistry (WRF/Chem) model and multiregi...
-
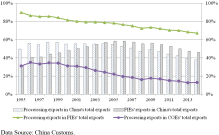
Revisiting the Global Net Carbon Dioxide Emission Transfers by International Trade: The Impact of Tr
To revisit global net carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions transfers by international trade for year 2007, this study employs a new world-wide, multiregional input-output (MRIO) table in which China's production is separated into domestic use, processing exports, and nonprocessing exports. The results show that processing exports in China involves relatively lower CO2 emissions than other production types for the same output levels. Therefore...
-
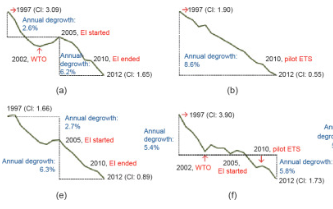
Performance Assessment and Outlook of China‘s Emission-Trading Scheme
China overtook the US as the world’s top emitter in 2007, and produced 1.5times the emissions of the US by 2013 [1] . At present, China’s emissions make up over a quarter of the global total. China is expected to produce three times the emissions of the US by 2030 [2] . Indeed, China’s role and efforts in CO 2 reductions matter greatly for the peaking of global emissions, even without further emission leakages to less-developed re...
-
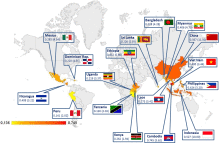
Carbon emissions embodied in international trade: The post-China era
The so-called post-China countries (PC-16́s), distinguished by low wages and high economic growth, will replace China as the “world’s factory”. The aim of this paper is to assess the effect of these changes on global CO 2 emissions pathways. To achieve this, a counterfactual is proposed wherein China’s trade with the rest of the world is replaced by the PC-16’s trade in a global multiregional input–output context. The emissi...
-
Firm ownership, China's export related emissions, and the responsibility issue
China's CO 2 emissions and those embodied in its exports have been extensively studied. One often neglected aspect is the prevalence of foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) in China's exports, for which a substantial portion of benefits return to the investing countries. In this paper, we revisit China's export-related CO 2 emission responsibilities by viewing them from a “new”, gross national income perspective. Using a recently deve...
-
China’s rising hydropower demand challenges water sector
Demand for hydropower is increasing, yet the water footprints (WFs) of reservoirs and hydropower and their contributions to water scarcity, are poorly understood. Here, we calculate reservoir WFs (freshwater that evaporates from reservoirs) and hydropower WFs (the WF of hydroelectricity) in China based on data from 875 representative reservoirs (209 with power plants). In 2010, the reservoir WF totaled 27.9 × 10 9 m 3 (Gm 3 ), or 22...
-
Physical and virtual water transfers for regional water stress alleviation in China
Water can be redistributed through, in physical terms, water transfer projects and virtually, embodied water for the production of traded products. Here, we explore whether such water redistributions can help mitigate water stress in China. This study, for the first time to our knowledge, both compiles a full inventory for physical water transfers at a provincial level and maps virtual water flows between Chinese provinces in 2007 and 20...
-
Revealing the Hidden Health Costs Embodied in Chinese Exports
China emits a considerable amount of air pollutants when producing goods for export. Previous efforts have emphasized the magnitude of export-related emissions; however, their health consequences on the Chinese population have not been quantified. Here, we present an interdisciplinary study to estimate the health impact of export-related air pollution. The results show that export-related emissions elevated the annual mean population wei...
-
Estimating inter-regional trade flows in China: A sector-specific statistical model
China has huge differences among its regions in terms of socio-economic development, industrial structure, natural resource endowments, and technological advancement. These differences have created complicated linkages between regions in China. In this study, building upon gravity model and location quotient techniques, we develop a sector-specific model to estimate inter-provincial trade flows, which is the base for making a multi-regio...
-
Tracing Primary PM2.5 emissions via Chinese supply chains
In this study, we examine a supply-chain approach to more effectively mitigate primary PM 2.5 emissions in China from the perspectives of production, consumption and their linkages using structural path analysis. We identify the pattern of all supply chain paths using principal component analysis. To address the severe haze problems in China, it is important to understand how final demand purchase initiates production processes and ulti...
-
The impact of domestic and foreign trade on energy-related PM emissions in Beijing
Particulate matter (PM) adversely affects air quality, human health and the climate, and it is more prevalent in urban areas. Few efforts have been made to quantify the impact of trade on PM concentrations in an urban economy. This paper presents an analysis of the impacts of domestic and international trade on PM emissions in Beijing using a three-scale input–output model, supported by the national and global embodied energy-related ...
-
A Hybrid‐Unit Energy Input‐Output Model to Evaluate Embodied Energy and Life Cycle Emissions for
We develop a hybrid‐unit energy input‐output (I/O) model with a disaggregated electricity sector for China. The model replaces primary energy rows in monetary value, namely, coal, gas, crude oil, and renewable energy, with physical flow units in order to overcome errors associated with the proportionality assumption in environmental I/O analysis models. Model development and data use are explained and compared with other approaches i...
-
Lifting China’s Water Spell
China is a country with significant but unevenly distributed water resources. The water stressed North stays in contrast to the water abundant and polluted South defining China’s current water environment. In this paper we use the latest available data sets and adopt structural decomposition analysis for the years 1992 to 2007 to investigate the driving forces behind the emerging water crisis in China. We employ four water indicators i...
-
China’s international trade and air pollution in the United States
China is the world’s largest emitter of anthropogenic air pollutants, and measurable amounts of Chinese pollution are transported via the atmosphere to other countries, including the United States. However, a large fraction of Chinese emissions is due to manufacture of goods for foreign consumption. Here, we analyze the impacts of trade-related Chinese air pollutant emissions on the global atmospheric environment, linking an economic-e...
-
Input-Output Analysis: The Next 25 Years
This year marks the 25th anniversary of the International Input–Output Association and the 25th volume of Economic Systems Research . To celebrate this anniversary, a group of eight experts provide their views on the future of input–output. Looking forward, they foresee progress in terms of data collections, methods, theory testing, and focus and scope....
-
Inter-provincial clean development mechanism in China: A case study of the solar PV sector
With ever growing urgency, climate change mitigation is fast becoming a priority for China. A successful policy of implementing and expanding sustainable development and the use of renewable energy is therefore vital. As well as long-term and near-term targets for installed capacity of renewable energy, in its 12th five-year plan, China has created strict and ambitious carbon intensity targets for each province. This study proposes an in...
-
Disaggregating the electricity sector of china’s input-output table for improved environmental lif
Missing process detail of sectors in Input–Output (I–O) tables has been pointed out as a limitation of I–O analysis in environmental-economic life cycle assessment. Aggregation of resource-intensive sectors decreases the accuracy of the results. Often, economic sectors are compiled in a more aggregated form than environmental satellite accounts, and as [Lenzen, M. (2011) Aggregation Versus Disaggregation in Input–Output Analysis ...
-
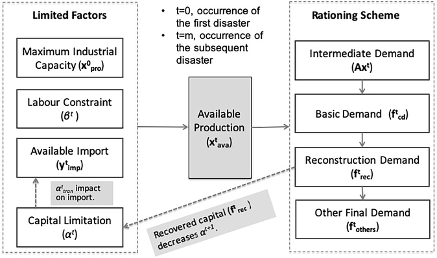
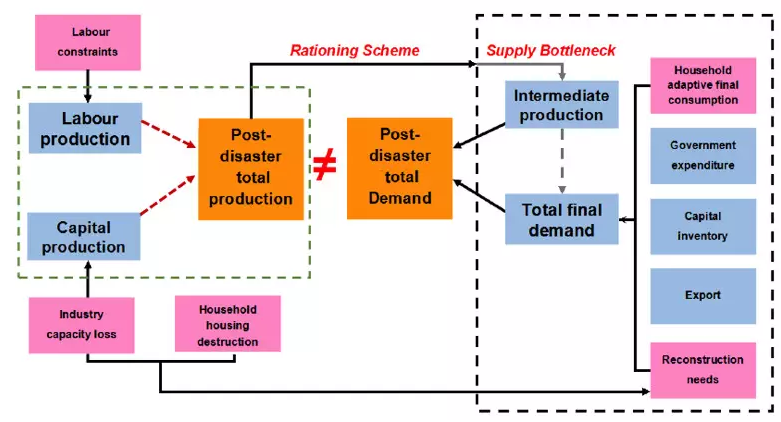
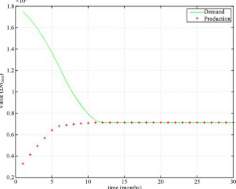
Modeling imbalanced economic recovery following a natural disaster using input-output analysis
Input-output analysis is frequently used in studies of large-scale weather-related (e.g., Hurricanes and flooding) disruption of a regional economy. The economy after a sudden catastrophe shows a multitude of imbalances with respect to demand and production and may take months or years to recover. However, there is no consensus about how the economy recovers. This article presents a theoretical route map for imbalanced economic recovery ...
-
Vulnerability of London’s Economy to Climate Change: Sensitivity to Production Loss
A variant of the Adaptive Regional Input-Output model (ARIO) has been developed to explore the sensitivity of the London economy to loss of production capacity in sectors affected by climate change related damage. The model is designed for linking to an Event Accounting Matrix (EAM) produced by climate and engineering teams, and then follow this damage through direct and indirect losses in the economy during a recovery process that is ei...
-
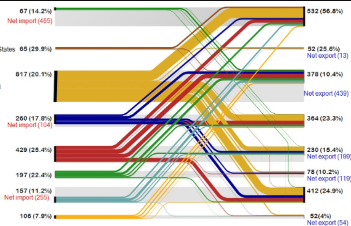
China’s inter-regional spillover of carbon emissions and domestic supply chains
In this study, we apply the inter-regional input–output model to explain the relationship between China’s inter-regional spillover of CO 2 emissions and domestic supply chains for 2002 and 2007. Based on this model, we propose alternative indicators such as the trade in CO 2 emissions, CO 2 emissions in trade and the regional trade balances of CO 2 emissions. Our results do not only reveal the nature and significance of inter-regiona...
-
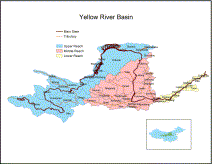
Assessing regional virtual water flows and water footprints in the Yellow River Basin, China: A cons
The Yellow River, the second longest river in China, is facing increasing water scarcity due to rising water consumption of a fast growing economy and an increasingly urbanized population with water-intensive consumption patterns. The Yellow River Basin (YRB) is divided into three regions: the upper, middle and lower reaches; each with very different characteristics in terms of water resources, economic structure and household income and...
-
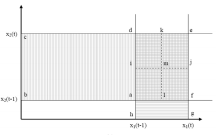
Disaggregating input-output models with incomplete information
Disaggregating a sector within the Leontief input–output (IO) framework is not a straightforward task since there is more than one possibility for the unknown technical coefficients of the disaggregated IO table, and more information than what is embodied in the aggregated IO table is thus required. This paper presents a methodology for disaggregating sectors into an arbitrary number of new sectors when the only available information a...
-
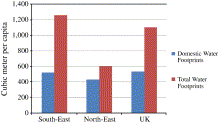
Spatially Explicit Analysis of Water Footprints in the UK
The Water Footprint, as an indicator of water consumption has become increasingly popular for analyzing environmental issues associated with the use of water resources in the global supply chain of consumer goods. This is particularly relevant for countries like the UK, which increasingly rely on products produced elsewhere in the world and thus impose pressures on foreign water resources. Existing studies calculating water footprints ar...
-
Assessing regional and global water footprints for the UK
The concept of the water footprint has been recently introduced as an important indicator for human-induced water consumption. The water footprint is defined as the total volume of water used during production and consumption of goods and services as well as direct water consumption by humans. Water is not only consumed directly but also indirectly in production processes. Therefore, calculating the water footprint enables us to quantify...
-
Input-Output Analysis and Carbon Footprinting: An overview of applications
This article provides an overview of how generalised multi-regional input–output models can be used for carbon footprint applications. We focus on the relevance and suitability of such evidence to inform decision making. Such an overview is currently missing. Drawing on UK results, we cover carbon footprint applications in seven areas: national emissions inventories and trade, emission drivers, economic sectors, supply chains, organisa...
-
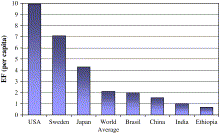
Environmental implications of urbanization and lifestyle change in China: Ecological and Water Footp
Since the open door policy in 1978 China has undergone enormous economic and social changes making China to be one of the largest economies and consumers of resources in the world. The pronounced differences in income and lifestyles especially between urban and rural China were also part of China's economic rebirth. This paper explores current trajectories and scenarios for urbanization and lifestyle changes and other important socio-eco...
-
A new and integrated hydro-economic accounting and analytical framework for water resources: A case
Water is a critical issue in China for a variety of reasons. China is poor of water resources with 2300m 3 of per capita availability, which is less than 1/3 of the world average. This is exacerbated by regional differences; e.g. North China's water availability is only about 271m 3 of per capita value, which is only 1/25 of the world's average. Furthermore, pollution contributes to water scarcity and is a major source for diseases, part...
-
Assessment of regional trade and virtual water flows in China
The success of China's economic development has left deep marks on resource availability and quality. Some regions in China are relatively poor with regards to water resources. This problem is exacerbated by economic growth. Flourishing trade activities on both domestic and international levels have resulted in significant amounts of water withdrawal and water pollution. Hence the goal of this paper is to evaluate the current inter-regi...